Common-mode Chokes
Find them on DigiKey under Filters -> Common Mode Chokes (CMC).
Common-mode chokes are good at filtering out high frequency common-mode noise. For filtering out differential-mode noise, see the Ferrite Bead page.
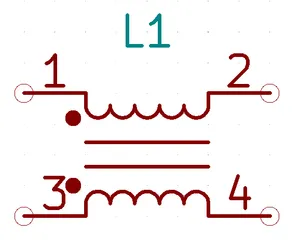
Schematic Symbol And Designator
A common-mode choke is typically drawn as two inductors separated by two lines. The two lines represent the inductive coupling between the two inductors. A common-mode choke has 4 pins. Typical designator prefixes are L (which is also used for a single inductor) or FL (for FiLter).
How It Works
A common-mode choke blocks common-mode noise (noise which is equal in voltage/current at the same time on two signals, typically power and ground). At this point you might be wondering, how can the current be going in the same direction down both wires, doesn’t the current need a return path? The key is to understand that common-noise finds a way back to it’s source through an external ground and capacitive coupling. The following diagram attempts to illustrate this:
The other type of noise, differential noise, is not blocked with a common-mode choke. To block differential noise, you need to use something such as a ferrite bead in a pi-filter configuration (the capacitors are not needed, but greatly help!).
Manufacturer Part Numbers
- BNX023-01L: Expensive but performant power-line filter by Murata.
Footnotes
-
Wurth Elektronik. WE-CMB Common Mode Power Line Choke [product page]. Retrieved 2024-08-24, from https://www.we-online.com/en/components/products/WE-CMB. ↩