Used in wire-wrap applications.
Cables
Cables are an important design consideration for most electrical designs and installations. They typically provide power and data (although wireless transmission is becoming more common for data transmission) to and between electronic.
Child Pages
Insulation Materials And Their Properties
| Common Name | Material | Temperature Range | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
ETFE | Ethylene tetraflouroethylene | -70 to +150°C | |
MG | Mica glass | 450°C |
|
mPPE | Modified polyphenylene ether | -40 to +105°C |
|
PDVF | Polyvinylidene fluoride | -40 to +125°C | Used in wire-wrap applications. |
PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene | -55 to +200°C |
|
PVC | Polyvinyl chloride | -40 to +90°C |
|
Silicone | Silicone | -40 to +150°C |
|
TGGT | Teflon-glass-glass-Teflon | +250°C |
|
XL-PVC | Cross-linked PVC | -55 to 105°C |
|
XLPE | Cross-linked polyethylene | -55 to 125°C |
|
Standards
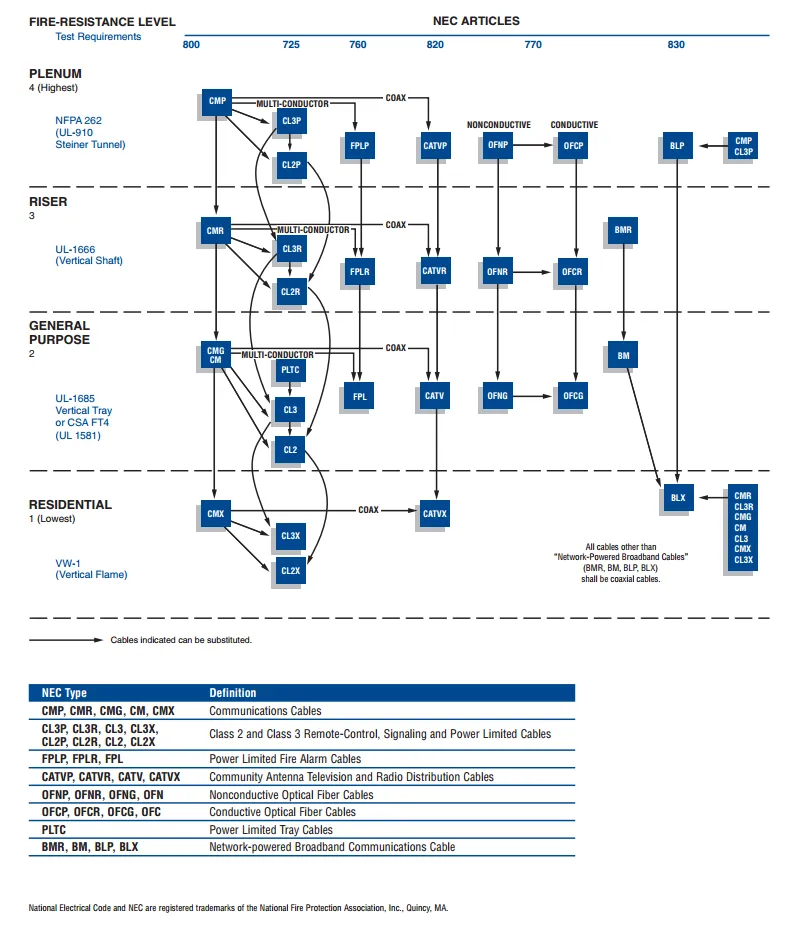
NEC
The National Electrical Code (NEC) is an American standards body which defines a set of standards for certain types of cabling and how they should be installed and used.
NEC types are acronyms consisting of a prefix describing cable type (e.g. coax, CATV, fibre optic) and a suffix indicating the type of flame test it has passed and where it can be installed.
Computer Cable
Computer cable can also be called “Security” or “Alarm” cable.
AWM
Underwriters Laboratories categorises some computer cable as appliance wiring material (AWM). It has become an industry standard. There are 5 different style numbers.
AWM cable is designed for the internal wiring of factory-assembled, “listed” appliances such as computers, white-wear, and industrial equipment.
UL2464
UL2464 is a loose standard defining some of the properties of computer cable, maintained by Underwriters Laboratories.
Reference standard: UL Subject 758, UL 1581 & CSA C22.2 No.210.2.
- Stranded, bare or tinned copper conductor
- Colour-coded SR-PVC insulation
- Cores cabled under aluminum mylar shield
- Tinned or bare copper stranded drain wire
- Tinned or bare copper wire braid shield up to 95% coverage
- Lead free PVC jacket
- Passes UL VW-1SC & CSA FT1 vertical flame test
Features Specifications: UL2464 Double Shielded Computer Cables
- Rated temperature: 80°C
- Rated voltage: 300V
Reference standard: UL Subject 758, UL 1581 & CSA C22.2 No.210.2
- Stranded, bare or tinned copper conductor
- Colour-coded SR-PVC insulation
- Cores cabled under aluminum mylar shield
- Tinned or bare copper stranded drain wire
- Tinned or bare copper wire braid shield up to 95% coverage
- Lead free PVC jacket
- Passes UL VW-1SC & CSA FT1 vertical flame test
Common Colours In UL2464 Cable:
- Black
- Brown
- Red
- Orange
- Yellow
- Green
- Blue
- Purple
- Gray
- White
- Pink
- Light Green
- Black-White
Common Colours For 12 Core Cable:
- Black
- Yellow
- Red
- Blue
- Green
- Yellow
- White
- Brown
- Violet
- Orange
- Pink
- Light Green
- Grey
Combined Power/Data Cable
Combined power/data cable refers to cable which makes special provision for carrying both moderate/large amounts of power and data through the same cable. All cables can carry “power” and data, but this category refers to two specific cases:
- The cable contains cores of different gauges, with the large gauge for carrying moderate to large amounts of power, and the smaller gauge for data.
- The cable contains both shielded, twisted pairs and non-shielded, non-twisted power cores.
Some examples of combined power/data cables include:
- Lapp UNITRONIC BUS PB COMBI 7-W cable. It contains 3x 1.0mm2 power cores and 1x2x0.64mm2 twisted pair core for data. The twisted pair is individually shielded (to protect it from noise on the power cores), and the whole cable is also shielded.
Mutual Capacitance
For cables with screening, typically a conductor-to-conductor and conductor-to-screen capacitance is given. The conductor-to-conductor capacitance is typically 80-140nF and the conductor-to-screen capacitance is typically 100-180nF (slightly higher than the conductor-to-conductor capacitance).
Screens
Cables (or specific cores within a cable) may be screened (a.k.a. shielded) to prevent electromagnetic radiation from both entering and exiting the cores within the cable. There are two primary ways to screen a cable:
- Copper braid: Braided strands of copper (or other conductive material, such as Aluminium) form the Faraday cage.
- Copper foil: A continuous flexible, thin sheet of copper of other conductive material is wrapped around the cables to form the Faraday cage.
The shield must be grounded (with respect to the signals/EMI) to be effective.
Cable Glands
Cable glands are strain-relief and weather-proofing glands which allow cables to be passed through enclosure walls.




