Coax Cable
Coaxial Cable
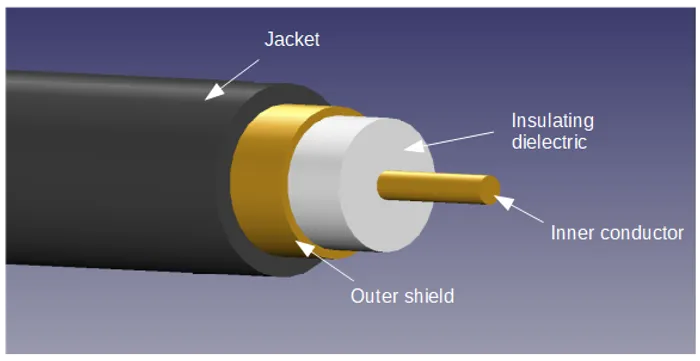
Coaxial cable (or just coax cable) is a type of cable consisting of single core surrounded by a circular outer shield, with a insulating dielectric sandwiched between the two. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and outer shield sharing the same axis (they are concentric with one another). Coax is most commonly used to transmit high frequency signals over small (oscilloscope probes) and large distances (transatlantic phone cables).
RG-6 is one of the most common types of coaxial cable in residual homes due to it’s use with TVs.
Properties of popular coaxial cable types:
| Name | Z_C | Conductor Diameter | Insulator Diameter | Shield Outer Diameter | Jacket Outer Diameter | Capacitance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RG-6 | 1.0mm | 4.57mm | 5.2mm | 6.6mm | 68pF/m 1 | |
| RG-58 | 5.0mm | 82pF/m2 | ||||
| RG-59 |
Properties of popular coaxial cable dielectrics3:
| Name | Propagation Velocity |
|---|---|
| Solid Polyethylene (PE) | 0.659c |
| Foam Polyethylene (FE) | 0.800c |
| Foam Polystyrene (FS) | 0.910c |
| Air Space Polyethylene (ASP) | 0.840-0.880c |
| Solid Teflon (ST) | 0.694c |
| Air Space Teflon (AST) | 0.850-0.900c |
where is the speed of light in a vacuum.
Precision Capacitors From Coaxial Cable
Coax cable has a capacitance of approx. 1pF/10mm, as measured between the central conductor and the outer shield. Precision capacitors for prototype/lab use can be from trimmed lengths of coax. cable.
References
Footnotes
-
Wikipedia (2021, Sep 7). RG-6. Retrieved 2022-01-31, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RG-6. ↩ ↩2
-
Wikipedia (2020, Dec 19). RG-58. Retrieved 2022-01-31, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RG-58. ↩ ↩2
-
RF Cafe. Coaxial Cable Specifications. Retrieved 2021-05-05, from https://www.rfcafe.com/references/electrical/coax-chart.htm. ↩

