Setting up MCUboot in Zephyr
Zephyr has built-in support for the MCUboot bootloader, a popular bootloader that also is supported by a number of other platforms/manufacturers such as Apache Mynewt, RIOT, Mbed OS, Espressif, and Cypress/Infineon.1
The MCUboot implementation for Zephyr supports Bluetooth bootloading. The Nordic nRF app can be used to bootload during development.
The most basic first thing you have to enable is CONFIG_BOOTLOADER_MCUBOOT=y:
CONFIG_BOOTLOADER_MCUBOOT=yOn start-up, MCUboot inspects the images in each of the slots to work out what type of swap to perform (if any). It decides to do one of the following:2
BOOT_SWAP_TYPE_NONE: This is the usual or “no upgrade” process, in which MCUboot boots the primary image.BOOT_SWAP_TYPE_TEST: Swaps the images and then boots the new primary image, but reverts back to the old image on the next reset. This will involve MCUboot swapping back the images on the next reset.BOOT_SWAP_TYPE_PERM: Swaps the images and then boots the new primary image.BOOT_SWAP_TYPE_REVERT: A previous test swap was not made permanent.BOOT_SWAP_TYPE_FAIL: The swap failed.BOOT_SWAP_TYPE_PANIC: An unrecoverable error occurred while swapping.
CONFIG_MCUBOOT_IMGTOOL_SIGN_VERSION is used to set the version.
CONFIG_MCUBOOT_IMGTOOL_SIGN_VERSION="1.0.0"Note that "0.0.0" is not allowed.
Magic Number
MCUboot uses a magic number to detect whether or not a slot contains a valid image. The magic number is long and random enough that it is statistically very unlikely to be present in memory unless it was purposely written. The magic number is written to the last 16 bytes of each image slot.
Confirming Images
At some point after you have booted up into you application and done some checks, you will want to tell MCUboot that the current image is “good”. You can do this with the boot_write_img_confirmed() function:
boot_write_img_confirmed();Erasing Images
You can remove images with boot_erase_img_bank(). This takes a bank number as an argument. With a simple setup, bank 0 is equal to slot 0 and bank 1 is equal to slot 1.
err = boot_erase_img_bank(1);if(err != 0){ LOG_ERR("Failed to erase image bank 1");}Bluetooth
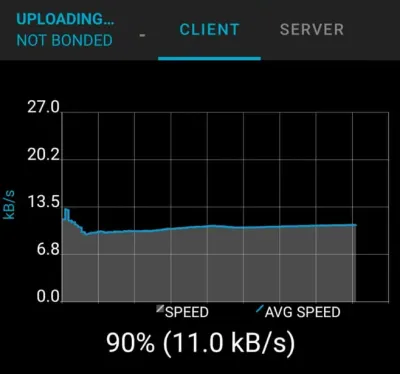
If bootloading via Bluetooth, don’t expect speeds greater than about 4-10 kB/s when uploading new firmware. This is a placeholder for the reference: fig-transfer-speeds-of-dfu-over-bluetooth shows the transfer speeds I managed to achieve over Bluetooth. It takes about 30-60 seconds to transfer the entire application image which was in the 200-400 kB range.
Logging
CONFIG_MCUBOOT_UTIL_LOG_LEVEL_DBG=y[00:00:00.372,039] <inf> mcuboot: Starting bootloader[00:00:00.379,364] <inf> mcuboot: Primary image: magic=good, swap_type=0x3, copy_done=0x1, image_ok=0x1[00:00:00.389,862] <inf> mcuboot: Secondary image: magic=good, swap_type=0x3, copy_done=0x3, image_ok=0x1[00:00:00.399,841] <inf> mcuboot: Boot source: none[00:00:00.406,372] <inf> mcuboot: Image index: 0, Swap type: perm[00:00:05.685,638] <inf> mcuboot: Starting swap using move algorithm.Footnotes
-
MCUboot. MCUboot - Secure boot for 32-bit Microcontrollers! [project homepage]. Retrieved 2024-01-27, from https://docs.mcuboot.com/. ↩
-
MCUboot. MCUboot - Design [documentation]. Retrieved 2025-08-28, from https://docs.mcuboot.com/design.html. ↩

