Zephyr Bluetooth
Nordic has contributed significantly to the Zephyr Bluetooth API ever since they adopted Zephyr as their official platform for the nRF52, nRF53 and nRF91 MCU families.
To enable Bluetooth in your Zephyr project, you need to enable the Bluetooth subsystem in your prj.conf file with CONFIG_BT=y.
CONFIG_BT=yRoles
Peripheral
Most Zephyr-based Bluetooth applications will act as a peripheral. A peripheral is a Bluetooth device that both advertising and allows connections. Enabling the peripheral role is done by setting the CONFIG_BT_PERIPHERAL configuration option.
CONFIG_BT_PERIPHERAL=yCONFIG_BT_DEVICE_NAME="MY_DEVICE"CONFIG_BT_DEVICE_APPEARANCE=1280The device appearance is an assigned number that describes the type of device. A full list of assigned numbers can be found here.
The bare minimal C code to get the Bluetooth peripheral advertising (and connectable) is:
#include <zephyr/bluetooth/bluetooth.h>#include <zephyr/kernel.h>
#define DEVICE_NAME CONFIG_BT_DEVICE_NAME#define DEVICE_NAME_LEN (sizeof(DEVICE_NAME) - 1)
static const struct bt_data ad[] = { BT_DATA_BYTES(BT_DATA_FLAGS, (BT_LE_AD_GENERAL | BT_LE_AD_NO_BREDR)), BT_DATA(BT_DATA_NAME_COMPLETE, DEVICE_NAME, DEVICE_NAME_LEN),};
static const struct bt_data sd[] = { BT_DATA_BYTES(BT_DATA_UUID128_ALL, BT_UUID_NUS_SRV_VAL),};
int main(void){ int err; err = bt_enable(NULL); __ASSERT(err == 0, "Failed to enable bluetooth: %d\n", err);
err = bt_le_adv_start(BT_LE_ADV_CONN, ad, ARRAY_SIZE(ad), sd, ARRAY_SIZE(sd)); __ASSERT(err == 0, "Failed to start advertising: %d\n", err);
while (1) { k_sleep(K_MSEC(1000)); }}Nordic UART Service
The Nordic UART Service (NUS) is a service that allows you to send and receive serial data over Bluetooth. You can enable it with:
CONFIG_BT=yCONFIG_BT_PERIPHERAL=yCONFIG_BT_DEVICE_NAME="Nordic_UART_Service"CONFIG_BT_MAX_CONN=1CONFIG_BT_MAX_PAIRED=1
# Enable the NUS serviceCONFIG_BT_NUS=yThe following C++ code shows a minimal example that configures a MCU as a Bluetooth peripheral and advertises a Nordic UART Service.
#include <bluetooth/services/nus.h>#include <zephyr/bluetooth/bluetooth.h>
static void bt_receive_cb( struct bt_conn *conn, const uint8_t *const data, uint16_t len){ int err; char addr[BT_ADDR_LE_STR_LEN] = {0};
bt_addr_le_to_str(bt_conn_get_dst(conn), addr, ARRAY_SIZE(addr));
LOG_INF("Received data from: \"%s\".", addr);}
static struct bt_nus_cb nus_cb = { .received = bt_receive_cb,};
static const struct bt_data ad[] = { BT_DATA_BYTES(BT_DATA_FLAGS, (BT_LE_AD_GENERAL | BT_LE_AD_NO_BREDR)), BT_DATA(BT_DATA_NAME_COMPLETE, DEVICE_NAME, DEVICE_NAME_LEN),};
static const struct bt_data sd[] = { BT_DATA_BYTES(BT_DATA_UUID128_ALL, BT_UUID_NUS_VAL),};
int main(void){ int err = bt_enable(NULL); __ASSERT(err == 0, "bt_enable() failed with error %d.", err);
err = bt_nus_init(&nus_cb); __ASSERT(err == 0, "bt_nus_init() failed with error %d.", err);
err = bt_le_adv_start(BT_LE_ADV_CONN_FAST_2, ad, ARRAY_SIZE(ad), sd, ARRAY_SIZE(sd)); __ASSERT(err == 0, "bt_le_adv_start() failed with error %d.", err);
return 0;}
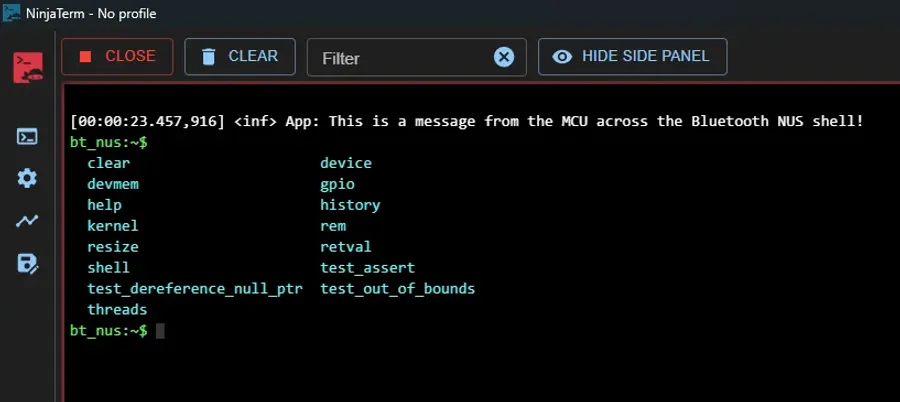
Bluetooth NUS Shell
Nordic provides an example project which let’s you configure the Bluetooth NUS service to use the Zephyr shell. This allows you to send and receive shell commands over Bluetooth, as well as view logs (just like a standard serial port based shell).
Update your prj.conf file with the configuration shown below. Note that most of the basic Bluetooth configuration remains the same as the basic Bluetooth NUS example above, except we replace CONFIG_BT_NUS=y with CONFIG_SHELL_BT_NUS=y.
CONFIG_BT=yCONFIG_BT_PERIPHERAL=yCONFIG_BT_DEVICE_NAME="Nordic_UART_Service"CONFIG_BT_MAX_CONN=1CONFIG_BT_MAX_PAIRED=1
# Enable the BT NUS shellCONFIG_SHELL_BT_NUS=y
# Don't enable this unless you need to debug the NUS shell logic, and watch out for infinite loops (see below)!# CONFIG_SHELL_BT_NUS_LOG_LEVEL_DBG=y
# Set the most verbose log level for any logs emitted across the Bluetooth NUS shell. Can also be _ERR, _WRN, _INF or _NONE.CONFIG_SHELL_BT_NUS_INIT_LOG_LEVEL_DBG=yAlthough you might want to think about increasing the MTU when sending large log messages for efficiency, I have found that can work ok on the default MTU because it is treated like a serial stream (a large log message will be broken up and sent in many smaller Bluetooth packets).
C++ Example Code
Here is an example of how to setup the Bluetooth NUS shell in a C++ project. Add the following to a Bluetooth.hpp file.
#pragma once
namespace my_firmware {
class Bluetooth {
public: ~Bluetooth();
static Bluetooth& getInstance();
void startAdvertising(); void onConnect(struct bt_conn *conn, uint8_t err); void onDisconnect(struct bt_conn *conn, uint8_t reason); void onRecycled();
private: struct bt_conn* m_currentConn = nullptr; Bluetooth();};
} // namespace my_firmwareAdd the following to a Bluetooth.cpp file:
// 3rd party includes#include <bluetooth/services/nus.h>#include <shell/shell_bt_nus.h>#include <zephyr/bluetooth/bluetooth.h>#include <zephyr/bluetooth/hci.h>#include <zephyr/logging/log.h>
// Local includes#include "Bluetooth.hpp"
LOG_MODULE_REGISTER(Bluetooth, LOG_LEVEL_INF);
namespace my_firmware {
#define DEVICE_NAME CONFIG_BT_DEVICE_NAME#define DEVICE_NAME_LEN (sizeof(DEVICE_NAME) - 1)
static void bt_receive_cb( struct bt_conn *conn, const uint8_t *const data, uint16_t len){ int err; char addr[BT_ADDR_LE_STR_LEN] = {0};
bt_addr_le_to_str(bt_conn_get_dst(conn), addr, ARRAY_SIZE(addr));
LOG_INF("Received data from: \"%s\".", addr);}
static struct bt_nus_cb nus_cb = { .received = bt_receive_cb,};
static const struct bt_data ad[] = { BT_DATA_BYTES(BT_DATA_FLAGS, (BT_LE_AD_GENERAL | BT_LE_AD_NO_BREDR)), BT_DATA(BT_DATA_NAME_COMPLETE, DEVICE_NAME, DEVICE_NAME_LEN),};
static const struct bt_data sd[] = { BT_DATA_BYTES(BT_DATA_UUID128_ALL, BT_UUID_NUS_VAL),};
static void connected(struct bt_conn *conn, uint8_t err){ Bluetooth::getInstance().onConnect(conn, err);}
static void disconnected(struct bt_conn *conn, uint8_t reason){ Bluetooth::getInstance().onDisconnect(conn, reason);}
static void recycled_cb(void){ Bluetooth::getInstance().onRecycled();}
BT_CONN_CB_DEFINE(conn_callbacks) = { .connected = connected, .disconnected = disconnected, .recycled = recycled_cb,};
Bluetooth& Bluetooth::getInstance(){ static Bluetooth instance(); return instance;}
Bluetooth::Bluetooth(){ LOG_INF("Initialising Bluetooth..."); int err = bt_enable(NULL); __ASSERT(err == 0, "bt_enable() failed with error %d.", err);
LOG_INF("Initialising the shell BT NUS service..."); err = shell_bt_nus_init(); __ASSERT(err == 0, "shell_bt_nus_init() failed with error %d.", err);
startAdvertising();}
Bluetooth::~Bluetooth(){}
void Bluetooth::startAdvertising(){ LOG_INF("Starting advertising..."); int err = bt_le_adv_start(BT_LE_ADV_CONN_FAST_2, ad, ARRAY_SIZE(ad), sd, ARRAY_SIZE(sd)); __ASSERT(err == 0, "bt_le_adv_start() failed with error %d.", err);}
void Bluetooth::onConnect(struct bt_conn *conn, uint8_t err){ char addr[BT_ADDR_LE_STR_LEN];
if (err) { LOG_ERR("Connection failed, err 0x%02x %s", err, bt_hci_err_to_str(err)); return; }
bt_addr_le_to_str(bt_conn_get_dst(conn), addr, sizeof(addr)); LOG_INF("Connected to \"%s\".", addr);
m_currentConn = bt_conn_ref(conn);
// Enable the shell through the NUS service shell_bt_nus_enable(conn);}
void Bluetooth::onDisconnect(struct bt_conn *conn, uint8_t reason){ char addr[BT_ADDR_LE_STR_LEN];
bt_addr_le_to_str(bt_conn_get_dst(conn), addr, sizeof(addr));
LOG_INF("Disconnected from \"%s\". Reason: 0x%02x (\"%s\").", addr, reason, bt_hci_err_to_str(reason));
if (m_currentConn) { bt_conn_unref(m_currentConn); m_currentConn = NULL; }
shell_bt_nus_disable();}
void Bluetooth::onRecycled(){ LOG_INF("Connection object available from previous conn. Disconnect is complete. Restarting advertising..."); startAdvertising();}
} // namespace my_firmwareSome of the key functions to note are:
shell_bt_nus_init(): This initialises the Bluetooth NUS shell. Called in the constructor of theBluetoothclass.shell_bt_nus_enable(): This enables the Bluetooth NUS shell. Called in the connect callback.shell_bt_nus_disable(): This disables the Bluetooth NUS shell. Called in the disconnected callback.
Then from your main.cpp file:
#include <zephyr/kernel.h>
// Local includes#include "Bluetooth.hpp"
void main(void){ // This will initialise the Bluetooth instance and start the advertising my_firmware::Bluetooth::getInstance();
while (1) { k_sleep(K_MSEC(1000)); }}Another example project can be found in the nrf-sdk GitHub repository (called shell_bt_nus).
If you want to connect to this Bluetooth NUS shell peripheral from a computer, you can use the NinjaTerm terminal application. This supports Bluetooth LE as a connection type, and can auto-detect and listen to the popular Bluetooth serial service and characteristic UUIDs such as the Nordic UART Service (NUS).
Another way to communicate with the peripheral is to use the desktop Python script provided by Nordic, which can be found here.
Update the LE Connection Interval
After you are connected, you can call bt_conn_le_param_update() to update the Bluetooth connection interval. This is useful if you want to save power by increasing the connection interval when you don’t need to send/receive data as often.
struct bt_le_conn_param conn_param = { .interval_min = (708), .interval_max = (800), .latency = (0), .timeout = (400), };int rc = bt_conn_le_param_update(conn, &conn_param);__ASSERT_NO_MSG(rc == 0);conn is a pointer to a struct bt_conn which is the connection object. It’s assumed you have that handy to pass in! The connection interval is in units of 1.25ms, so the above code sets the connection interval min. to 885ms and the max. to 1000ms. By default the min. and max were set to 15ms and 30ms respectively, so this is a significant slow down and results in good power savings for small battery powered devices. The timeout is in units of 10ms, so the above code sets the timeout to 4s. You can use the helper macro BT_LE_CONN_PARAM() to create the struct bt_le_conn_param object if you want.
If you are a Bluetooth central device, these settings will take effect. If you a peripheral device, these settings are “suggestions”. They are sent to the central device and it is up to the central device to accept them. The central device may reject them or choose other values.