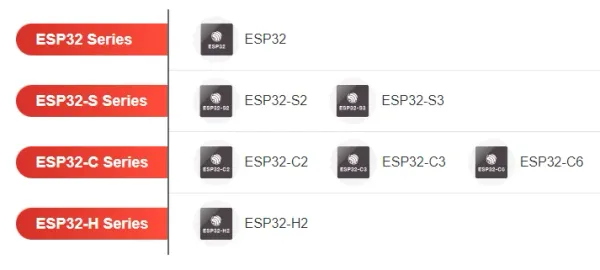
ESP32
ESP32 is a series of low-cost, low-power SoC microcontrollers designed by Espressif Systems.
The ESP32 range is supported by the ESP-IDF framework.
Serial Bootloader
ESP32-S3’s have serial bootloaders permanently baked into their ROM, and can talk to a host computer running esptool.py over a USB serial connection. The serial protocol is described here.
To get around limitations with a permanently unmodifiable bootloader, the first thing esptool.py does when it connects is to upload a flasher stub (a.k.a. “stub loader” or “stub”) to the ESP32 SoC. This stub loader than essentially takes over as the bootloader, and can provide extra functionality or fix bugs in the ROM bootloader1.
ESP-IDF
ESP-IDF provides a FreeRTOS port that supports both the Xtensa and RISC-V architectures used by ESP SoCs. ESP-IDF provides different versions of FreeRTOS in order to support SMP (symmetric multiprocessing) on 2-core ESP SoCs. There is also the option of using the Amazon SMP FreeRTOS which supports any number of cores2. ESP-IDF uses CMake as it’s build system.
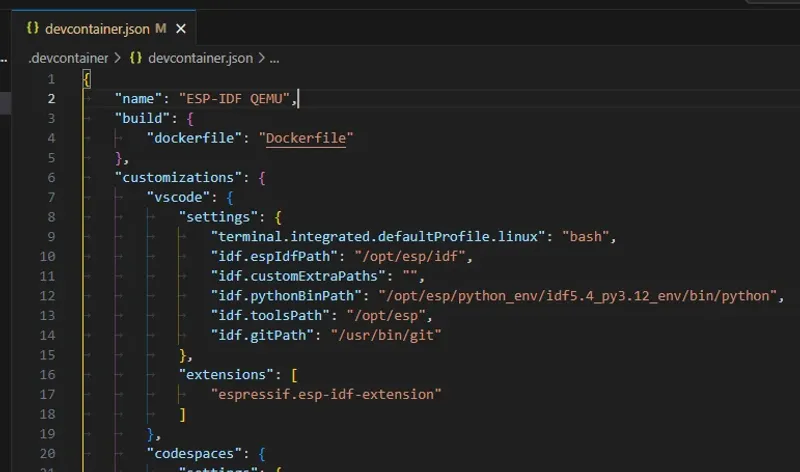
ESP-IDF supports dev containers. There is a Docker image pushed to Docker Hub that can be used for both dev containers and CI/CD pipelines. It contains ESP-IDF plus all of the additional tools required to build a ESP-IDF based project4. It is tagged with the ESP-IDF version.
Post-built Commands
To add a post-build command to a CMake-based ESP-IDF project, you can use the add_custom_command() function, targeting the gen_project_binary target and with the POST_BUILD argument. This function allows you to specify a shell command that should be executed after the build process has completed.
add_custom_command( TARGET gen_project_binary POST_BUILD COMMAND echo "My custom command that runs after the project binary has been built.")Be aware that the shell command may make the project platform dependent. You could couple this with if(CMAKE_HOST_WIN32) style conditionals to run OS specific commands. You can see where the target gen_project_binary is defined in the ESP-IDF code here. app is another valid target you could use to run commands on.
esptool
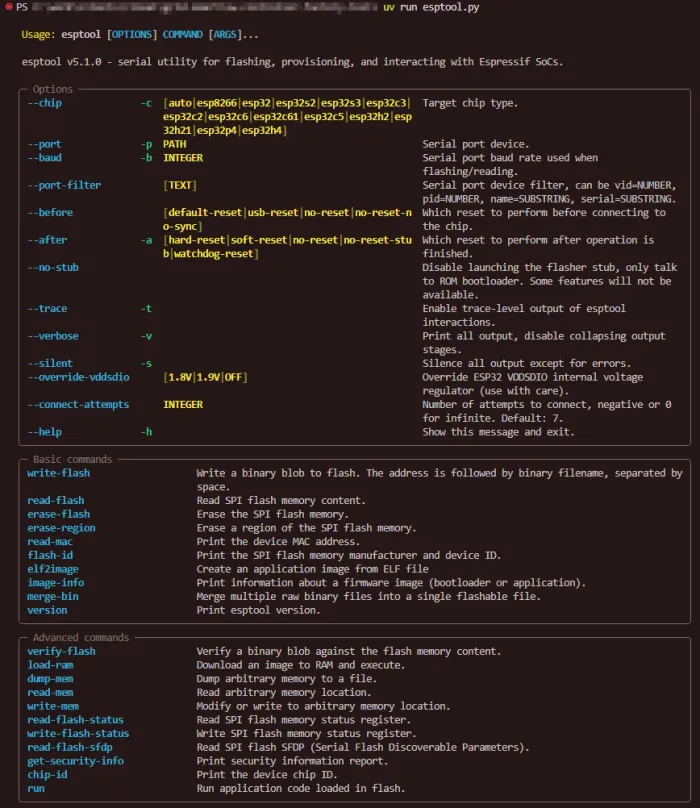
esptool is a Python based open-source tool for programming and otherwise interacting with a range of Espressif SoCs. It is cross-platform and supports Windows, macOS and Linux.5 It can be used as a command-line tool (the most common way) or as a Python library.
There are alternatives to esptool for different languages:
- esptool.js: A JavaScript port of esptool that can work both in Node.js and in the browser (it used the Web Serial API to work in the browser).
- espflash: A Rust port of esptool.
ESP32-C6
The ESP32-C6 is a SoC by Espressif Systems designing for wireless connectivity. It supports Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5 LE, Thread and Zigbee. It contains two cores - a high performance (HP) 32-bit RISC-V core at up to 160 MHz, and a low power (LP) 32-bit RISC-V core at up to 20 MHz. It comes in a QFN-40 or QFN-32 package.6
The ESP32-C6 is available as either a standalone IC or as a module (which provides things such as auxiliary components and an antenna). As of November 2025, there was four modules available:
- ESP32-C6-MINI-1
- ESP32-C6-MINI-1U
- ESP32-C6-WROOM-1
- ESP32-C6-WROOM-1U
The modules with the U suffix have an IPEX antenna connector instead of an internal PCB antenna.
The ESP32-C6 has a “USB-Serial-JTAG” peripheral which can be used to program the device over USB. Note that it cannot be used for general purpose USB communication, it is only for programming the device and debugging (e.g. logs). If connected to a computer via USB, it will enumerate as a serial device and a USB JTAG/serial debug unit. The VID will be 0x303A (Espressif uses this for all their products). The PID will likely be 0x1001 or close to this.7
When connected to a computer running Windows, it will enumerate as two different devices in the Device Manager:7
- COMx under “Ports (COM & LPT)”.
- USB JTAG/serial debug unit under “Universal Serial Bus devices”.
By default, the USB-Serial-JTAG peripheral is enabled. It can be disabled in firmware if wished so that you can use the D+/D- pins for something else such as GPIO. But if you do this, you will loose the ability to program via USB. There is a boot control pin which can be used to enter boot mode if USB is unavailable.7
Footnotes
-
Espressif Systems. esptool.py > Flasher Stub [documentation]. Retrieved 2024-10-18, from https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esptool/en/latest/esp32s3/esptool/flasher-stub.html. ↩
-
Espressif Systems. ESP-IDF - API Reference > System API > FreeRTOS [documentation]. Retrieved 2024-10-15, from https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/stable/esp32/api-reference/system/freertos.html. ↩
-
Espressif Systems. ESP-IDF. Retrieved 2024-10-15, from https://idf.espressif.com/. ↩
-
dockerhub. espressif/idf [docker image]. Retrieved 2024-10-15, from https://hub.docker.com/r/espressif/idf. ↩
-
Espressif Systems. espressif/esptool [GitHub repository]. Retrieved 2025-11-10, from https://github.com/espressif/esptool. ↩
-
Espressif Systems. Hardware > ESP32-C > ESP32-C6 [product page]. Retrieved 2025-11-10, from https://www.espressif.com/en/products/socs/esp32-c6. ↩
-
Espressif Systems. USB Host & Device > USB Host & Device > USB-Serial-JTAG Peripheral Introduction [documentation]. Retrieved 2025-11-10, from https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-iot-solution/en/latest/usb/usb_overview/usb_serial_jtag.html. ↩ ↩2 ↩3