Linear Programming
Overview
This page provides an introduction to linear programming, with examples which use GNU Linear Programming Toolkit C API.
What Is Linear Programming Good For?
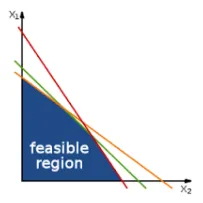
Linear programming is good for **solving problems in the below form:
The objective function is the function we want to either maximise or minimise. In the above example, this is:
is the value we want to maximise, and it is dependent on . The constraints are the equations which the solution is “subject to”. These are the following lines:
These limit the values of . You can also have bounds for these variables, such as:
However, these bounds are just another way of writing a constraint. In fact, the above bound can be written in constraint equation form as:
GLPK
Building GLPK
The GLPK source code can be downloaded from https://www.gnu.org/software/glpk/. This then has to be compiled/built for your computer.
Solving The Example In GLPK
GLPK can either (where the structural variables, x1, x2, … are allowed to vary continuously) or perform mixed-integer programming, where the structural variables must take on a integer number. A sub-set of mixed-integer programming is binary programming, where the structural variables are only allowed to be the integers 0 or 1.
Silencing GLPK
By default, glpk prints a small amount of information to the terminal when the solver is run. To silence this, call:
glp_term_out(GLP_OFF);