TRIACs
A TRIAC is a 4-layer semiconductor device that conducts current in either direction when given a signal.
The name TRIAC is a generic trademark and is an abbreviation of TRIode for Alternating Current. The formal names for a TRIAC are bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor, although these names are rarely used.
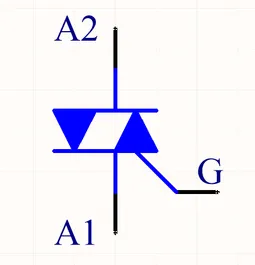
Schematic Symbol
The schematic symbol for the TRIAC is shown below:
The anodes A1 and A2 may be called Main Terminal 1 (MT1) and Main Terminal 2 (MT2) respectively.
Component Parameter Descriptions
Repetitive Peak Off-State Voltage (50-60Hz)
The maximum repetitive peak voltage () allowed across the device. Remember that RMS voltage readings need to be multiplied by to find the peak voltage (assuming a sinewave).
Non-repetitive Off-State Voltage
The maximum off-state peak voltage across A1 and A2 that is non-repetitive. Normally this is defined to pulses less than 10ms wide.
Gate Currents
A “normal” TRIAC might have a gate trigger current () of 20-50mA. A “sensitive” TRIAC might have an of 2-10mA.
Part Numbering
Many TRIACs begin with/include the three-letter term BTA.