RS-422 Protocol
RS-422 (a.k.a. TIA/EIA-422) is a serial, differential communication protocol used for transmitting data. RS-422 uses 2 wires for transmitting and 2 wires for receiving for full-duplex communication. 1 driver and up to 10 receivers can be connected per twisted pair, which is called simplex multidrop1 (unlike RS-485, which is differential and allows for multiple drivers). It is closely related to the less popular RS-423 protocol. It is also related to the RS-232 (single-ended) and RS-485 (differential) communication protocols.
| Speed | Max. Distance |
|---|---|
| 10kbps | 1200m2 |
| 10Mbps | 10m |
The maximum allowed differential voltage is (\pm 6.0V)2.
A mark (binary 1) is transmitted with a negative differential voltage, a space (binary 0) is transmitted with a positive differential voltage. This is the same terminology and “inverse” polarity as RS-232 and RS-485.
Connectors
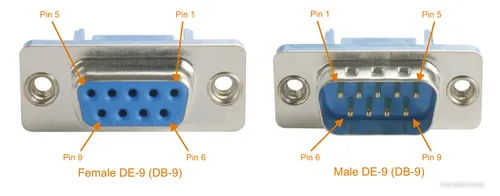
The DE-9 is the de facto industry standard connector for RS-422.
DE-9 (DB-9)
The industry standard pinout for RS-422 in a DE-9 connector is shown in the table below3.
| Pin Num. | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TXD- | Transmitted data - |
| 2 | TXD+ | Transmitted data + |
| 3 | RTS- | Request to send - |
| 4 | RTS+ | Request to send + |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
| 6 | RXD- | Received data - |
| 7 | RXD+ | Received data + |
| 8 | CTS- | Clear to send - |
| 9 | CTS+ | Clear to send + |
DB-25
The D-Subminiature DB-25 connector is another popular choice for carrying RS-422 signals.
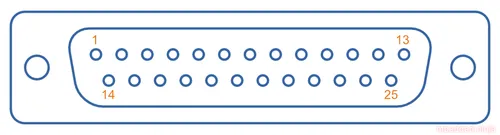
Industry standard pinout for RS-422 on a DB-25 connector4:
| Pin Num. | Name | Description | Pin Num. | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | EGND | Earth ground | 14 | TXD+ | Transmitted data + |
| 2 | TXD- | Transmitted data - | 15 | CLK- | Transmit clock - |
| 3 | RXD- | Received data - | 16 | RXD+ | Received data + |
| 4 | RTS- | Request to send - | 17 | CLK+ | Receiver clock - |
| 5 | CTS- | Clear to send - | 18 | - | Unassigned |
| 6 | DSR | Data set ready | 19 | RTS+ | Request to send + |
| 7 | GND | Logic ground | 20 | DTR- | Data terminal ready - |
| 8 | DCD- | Data carrier detect - | 21 | Signal quality detect | |
| 9 | Reserved | 22 | - | Unassigned | |
| 10 | Reserved | 23 | DTR+ | Data terminal ready + | |
| 11 | - | Unassigned | 24 | CLK+ | Transmit clock + |
| 12 | DCD+ | Data carrier detect | 25 | CLK+ | Receiver clock + |
| 13 | CTS+ | Clear to send |
Parts
Many RS-422 transceivers also support RS-485.
| Manf. Part Num. | Manf. | Protocols | (V_S) | Data Rate | Package | USD, 100 | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renesas | RS-422, RS-485 | 3-3.6V | 40Mbps | DFN-10 | Also supports RS-485. |
Footnotes
-
Manny Soltero, Jing Zhang, Chris Cockril (2002, Jun). SLLA070D: RS-422 and RS-485 Standards Overview and System Configurations (Application Report). Retrieved 2022-02-06, from https://www.ti.com/lit/an/slla070d/slla070d.pdf. ↩
-
Wikipedia (2022, Jan 25). RS-422. Retrieved 2022-02-05, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RS-422. ↩ ↩2
-
ActiveXperts. RS422 Serial Port Connector Pin Layout. Retrieved 2022-02-06, from https://www.activexperts.com/serial-port-component/tutorials/pinout422/. ↩
-
Michael R. Sweet (1999). Serial Programming Guide for POSIX Operating Systems. Retrieved 2022-02-12, from https://www.cmrr.umn.edu/~strupp/serial.html. ↩