Ethernet Protocol
History
Originally, ethernet used a single coax cable (10base2).
Components
Connector
RJ45 jack. Connectors which integrate the magnetics are called integrated connector modules (ICMs).
Magnetics
Magnetics are part of the Ethernet specification for all xBASE-T networks (which includes pretty much every Ethernet PHY standard except for the first StarLAN-1, StarLAN-10 and LattisNet).
There are two options for magnetics, either:
. Buy a ethernet magnetics component for your PCB. . Buy a jack (connector) which already has the magnetics integrated into it. Connectors which integrate the magnetics are called integrated connector modules (ICMs).
Physical Layer (PHY)
The PHY is the circuitry which drives the magnetics.
MAC
Standards
Many of the IEEE Ethernet standards are in a form similar to 10BASE-T. In this example, the 10 represents a throughput of 10 Mbps, BASE is because it uses baseband transmission (the twisted pairs can transmit frequencies all the way down to DC), and the T indicates the transmission medium used.1 G is added to the throughput to indicate Gbps, e.g. 5GBASE-T is a throughput of 5 Gbps.
10BASE-T
Used Cat 3 cable.
10BASE-T1L
Designed for automotive and IoT applications.
10BASE-T1S
Designed for automotive and IoT applications. Allows for a multi-drop architecture.
Ethernet Jacks
Some ethernet jacks come with the magnetics already in-built, saving you the trouble of including them yourself on the mounted-to PCB
Power Over Ethernet (PoE)
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is the term used to describe ethernet cables/systems that also provide a power source over the same cable as the data. Typically 44-57VDC (48V is a common choice) is passed over one or more of the twisted pairs in most ethernet cables. Data and power can be transmitted along the same twisted pairs as long as proper transformer-based extraction (center-tapped isolation transformers) of the AC data signal and DC power is used. The early PoE standards could provide around 10W of power, but the newer standards allow up to approx. 75W.
Power sourcing equipment (PSE) are the devices that provide power onto the ethernet bus. The powered device (PD) is the device on the other end of the cable which is consuming the power. The PDs can be up to 100m away from the PSE (as defined by the existing Ethernet standard, this is unchanged with the introduction PoE).
A PoE injector is a stand-alone device used to add (“inject”) DC power into an existing Ethernet cable.
The assured power is the amount of power available to the powered device at the end of cable. This is less than the power outputted by the PSE due to the energy lost in the impedance of the cabling.
| Name | IEEE standard | Year | Power to PD | Max. power per port | Energized pairs | Supported devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PoE | IEEE 802.3af (Type 1) | 2003 | 12.95 W | 15.4 W | 2-pair | VoIP phones, WAP |
| PoE+ | IEEE 802.3at (Type 2) | 2009 | 25.5 W | 30 W | 2-pair | |
| PoE++ (UPoE) | IEEE 802.3bt (Type 3) | 51 W | 60 W | 4-pair | ||
| PoE++ | IEEE 802.3bt (Type 4) | 71.3 W | 100 W | 4-pair | Tilt/pan/zoom (PTZ) security cameras. |
PoE++ is also known as 4PPoE. UPoE is an acronym for Ultra Power over Ethernet.
Signature resistance of 25kR.
Single Pair Ethernet (SPE)
Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) is a version of Ethernet which uses a single twisted pair. Coupled with PoDL (Power over Data Lines), it is impressive that a single twisted pair can be both used to send bi-directional data (~10Mbps) and power (~50W) over the same cable!
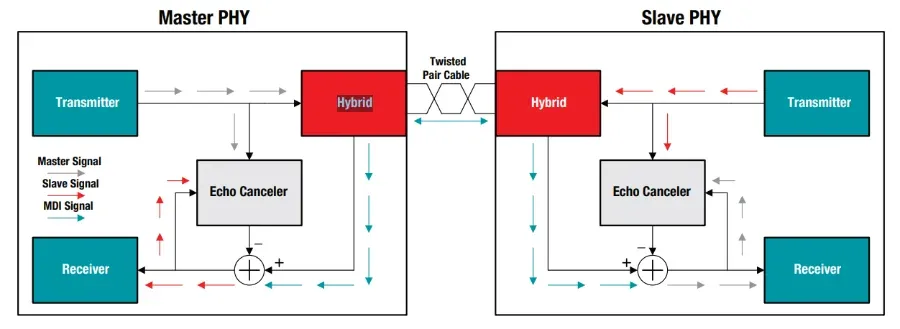
Bi-directional data over the same pair works by the principle of superposition. Each side has echo cancellation which is used by their receiver to cancel out their own transmitted signal, leaving behind the component of the waveform which was sent from the other side.2
All SPE standards have -T1 in their name, since the 1 refers to a single twisted pair.
| Year | Standard | Speed | Max. Distance | Symbol Rate | BER | Duplex | PoDL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | IEEE 802.3cg | 10BASE-T1S | 10 Mbit/s | 25 m | UTP | 12.5 MHz | 1 x 10-9 | HD | No |
| 10BASE-T1L | 1000 m | STP | 7.5 MHz | 1 x 10-10 | FD | Yes | |||
| 2015 | IEEE 802.3bw | 100BASE-T1 | 100 Mbit/s | 15 m | UTP | 66.6 MHz | |||
| 25 m | STP | ||||||||
| 2016 | IEEE 802.3bp | 1000BASE-T1 | 1000 Mbit/s | 15 m | Type A | 750 MHz | |||
| 40 m | Type B | ||||||||
| 2020 | IEEE 802.3ch | 2.5GBASE-T1 | 2.5 Gbit/s | 15 m | STP | 1.4 GHz | |||
| 5GBASE-T1 | 5 Gbit/s | 2.8 GHz | |||||||
| 10GBASE-T1 | 10 Gbit/s | 5.6 GHz | |||||||
Automotive Ethernet
Automotive Ethernet (formerly called BroadR-Reach or OABR (Open Alliance BroadR-Reach)) can be thought of as a subgroup of SPE. It uses the same single twisted pair cable, but defines additional high-level protocols on top of the SPE protocol.4
It is a popular choice for automotive applications which is gaining momentum against the more traditional CAN bus for the backbone of the vehicle network.
Power over Data Lines (PoDL)
Power over Data Lines (PoDL) is the name given to the trick of powering devices over single pair ethernet by injecting a DC voltage and superimposing it with the signal onto the single twisted pair cable. The IEEE 802.3bu-2016 amendment first introduced PoDL for SPE standards 100BASE-T1 and 1000BASE-T1. It is now defined for all SPE standards including 100BASE-T1, 1000BASE-T1, 2.5GBASE-T1, 5GBASE-T1 and 10GBASE-T1.5
The standard names a device which provides power as Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) and a device which consumes power as the Powered Device (PD).3
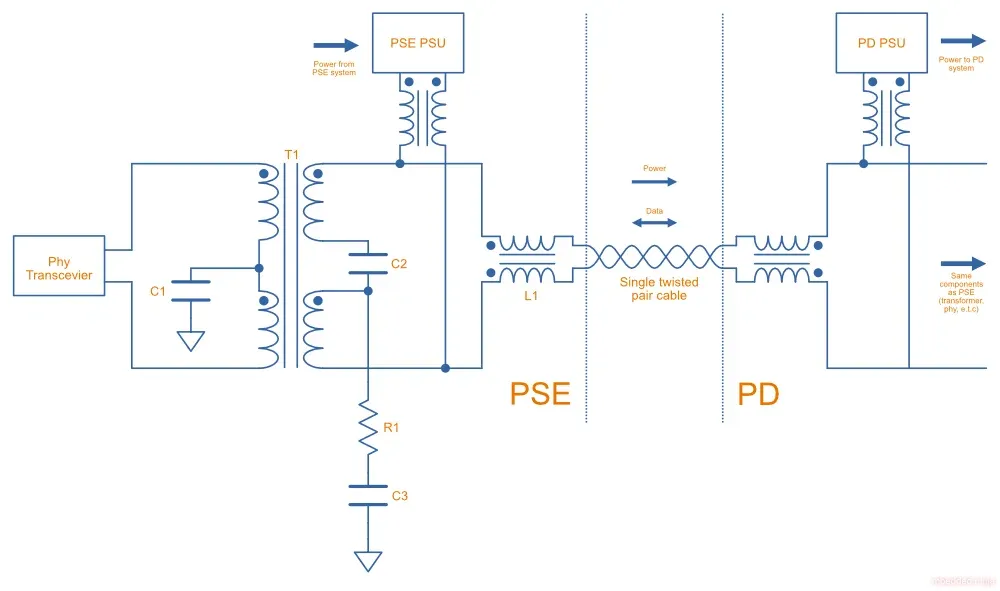
This is a placeholder for the reference: fig-spe-with-podl-diagram is a schematic showing the core component used to build a SPE with PoDL system.
Conventional IEEE 802.3 multipair Ethernet (including PoE) requires galvanic isolation from the chassis ground. According to IEEE 802.3bu (PoDL) and IEEE 802.3cg (SPoE) standards, PSE/PDs must provide at least 1 MΩ (@ 5 V ± 20%) isolation between all accessible external conductors and the interface (MDI).3
When PSE wants to provide power to a PD device, it first attempts to detect a PD device, and then classify it using a process called SCCP.6 The protocol also uses Cable Resistance Measurement (CRM) to assess the quality of the connection.3
For convenience, the standard allows the DC voltage to applied in either direction by the power sourcing equipment. This means that the receiver requires a rectifier (or similar) to support reverse polarity.6
This is a placeholder for the reference: tbl-podl-classes is a summary of the different PoDL classes defined in the IEEE standards and the various voltages, currents and powers supported by each class.
| Class | Standard | Class Type | V_PSE(max) (V) | V_PSE(min) (V) | I_PI(max) (mA) | P_PD(max) (W) | V_PD(min) (V) | Cable (AWG) | Cable length (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | IEEE 802.3bu | 12V unregulated | 18 | 6 | 101 | 0.5 | 4.94 | - | - |
| 1 | IEEE 802.3bu | 12V unregulated | 18 | 6 | 227 | 1 | 4.41 | - | - |
| 2 | IEEE 802.3bu | 12V regulated | 18 | 14.4 | 249 | 3 | 12 | - | - |
| 3 | IEEE 802.3bu | 12V regulated | 18 | 14.4 | 471 | 5 | 10.6 | - | - |
| 4 | IEEE 802.3bu | 24V unregulated | 36 | 12 | 97 | 1 | 10.3 | - | - |
| 5 | IEEE 802.3bu | 24V unregulated | 36 | 12 | 339 | 3 | 8.86 | - | - |
| 6 | IEEE 802.3bu | 24V regulated | 36 | 26 | 215 | 5 | 23.3 | - | - |
| 7 | IEEE 802.3bu | 24V regulated | 36 | 26 | 461 | 10 | 21.7 | - | - |
| 8 | IEEE 802.3bu | 48V regulated | 60 | 48 | 735 | 30 | 40.8 | - | - |
| 9 | IEEE 802.3bu | 48V regulated | 60 | 48 | 1360 | 50 | 36.7 | - | - |
| 10 | IEEE 802.3cg | 24V | 30 | 20 | 92 | 1.23 | 14 | 18 | 1000 |
| 11 | IEEE 802.3cg | 24V | 30 | 20 | 240 | 3.2 | 14 | 14 | 1000 |
| 12 | IEEE 802.3cg | 24V | 30 | 20 | 632 | 8.3 | 14 | 24 | 1000 |
| 13 | IEEE 802.3cg | 55V | 58 | 50 | 231 | 7.7 | 35 | 18 | 1000 |
| 14 | IEEE 802.3cg | 55V | 58 | 50 | 600 | 20 | 35 | 14 | 1000 |
| 15 | IEEE 802.3cg | 55V | 58 | 50 | 1579 | 52 | 35 | 24 | 300 |
Class 15 provides the highest power output at 52 W.
PoDL Detection Phase
The detection phase is when the PSE tried to detect a PD device. The PSE sources a constant current between 9 and 16 mA with an open-loop voltage of 4.75 and 5.5 V. The PSE measures the voltage across the cable. If it is between 4.05 and 4.7 V the PSE concludes that a valid PD device is present.7
PoDL Classification Phase
Classification is done after detection and is when the PSE classifies the PD device into a specific class. This is done using a simple low speed one-wire protocol called SCCP. It is a pull-up, drive low protocol similar to I2C but with just the one wire. PSE provides the pull-up via a current source. Both the PSE and the PD can drive the line low by switching a transistor to ground.
Every SCCP transaction begins with the PSE driving the line low. If the PSE is transmitting, it drives it low to a set period of time. Different low durations determine whether a 0 or a 1 is sent. If the PD is transmitting, the PSE still drives the line low initially but then the PD takes over and holds it low for a set duration to determine a 0 or 1. Each bit is defined to take within 2.7 and 3.3 ms. If we assume the average of 3 ms, this makes the bandwidth a rather slow 333 bps. This is slow enough for MCUs to directly implement in firmware (i.e. no dedicated hardware peripheral required).7
Example ICs
DP83TC Family
The Texas Instruments DP83TC is a family of ethernet PHY ICs.
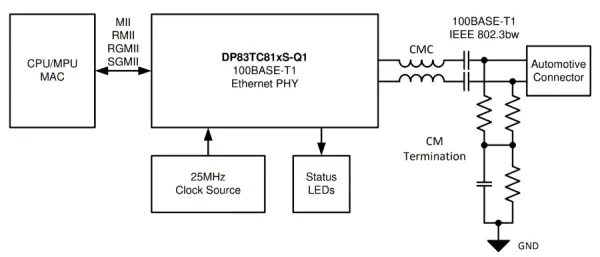
For example, the DP83TC813S-Q1 is a 100BASE-T1 PHY in a VQFN-28 package. It supports either MII, RGMII, RMII, or SGMII interfaces with the host MCU. This is a placeholder for the reference: fig-ti-dp83tc813s-q1-100base-t1-phy-simplified-application-schematic shows a simplified application schematic for the DP83TC813S-Q1.
EtherCAT
EtherCAT is a communication protocol with it’s physical layer following the Ethernet standard in IEEE 802.3 (the magnetics and PHY are the same). However, the similarity somewhat stops there, it uses a novel technique where:
- Each device is daisy chained to the next via Ethernet cable.
- The master emits a Ethernet frame (telegram).
- Each slave device reads the data addressed to it “on the fly”, and inserts it’s own data into the frame “on the fly”.
- Propagation times between slaves are only limited by hardware propagation delays.
The master node can be implemented using any device with standard Ethernet capability, the same magnetics, PHY and MAC is used. However, whilst the slave node use the same magnetics and PHY, the MAC is replaced by a special EtherCAT Slave Controller (ESC) which can process frames on the fly.
lwIP
lwIP is a BSD-licensed implementation of the TCP/IP protocol suite with a focus on small resource (RAM and flash memory) usage. It is designed for embedded systems, and requires only 10’s of kB of free RAM and 40kB’s of ROM (e.gc. flash)9.
It has support for IP, IPv6, UDP, TCP, ARP, PPPoE and more9.
Popular Chips
WIZnet W5xxx Family
The WIZnet W5xxx family of serial-to-ethernet ICs is very popular in the maker community. This family of ICs is used by the Arduino Ethernet board are Arduino Ethernet Shield.
- W5200: This chip implements the PHY, the TCP/IP stack (fully hardwired), and the 10/100 MAC Ethernet MAC, in a QFN-48 package. It uses the SPI Protocol to talk to a microcontroller. It’s power save features include power-down mode and WOL (wake on LAN). It runs of 3.3V but has 5V I/O tolerance.
- W5500: Supports up to 8 independent sockets (i.e. 8 different connections to different ports). Contains a 10BaseT/100BaseTX PHY. Like the W5200 is runs of 3.3V but has 5V I/O tolerance.

Microchip LAN867x Family
Microchip’s LAN8670, LAN8671 and LAN8672 are ethernet PHY ICs that use [^10BASE-T1S, 10BASE-T1S], allowing a multi-drop architecture of “at least 8 nodes and a minimum 25m of length”.
Footnotes
-
Wikipedia (2025, May 11). Baseband [wiki]. Retrieved 2025-10-29, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baseband. ↩
-
Donovan Porter (2018, Apr). 100BASE-T1 Ethernet: the evolution of automotive networking. Texas Instruments. Retrieved 2025-11-05, from https://www.ti.com/lit/wp/szzy009/szzy009.pdf. ↩ ↩2
-
Wurth Elektronik. Reference Design RD041 - Design of a Single Pair Ethernet System with Power over Data Lines (SPoE). Retrieved 2025-10-28, from https://www.we-online.com/files/pdf1/rd041b_design-of-a-single-pair-ethernet-system-with-power-over-data-lines-spoe-v1.pdf. ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4 ↩5 ↩6
-
Vector (2023-03-21). Difference between Automotive and Standard Ethernet Technologies [KnowledgeBase article]. Retrieved 2025-11-02, from https://support.vector.com/kb?id=kb_article_view&sysparm_article=KB0013990&sys_kb_id=97ff00263b67eed0c1dc1d24c3e45aff&spa=1. ↩
-
Wikipedia (2025, Oct 25). Power over Ethernet [wiki]. Retrieved 2025-10-29, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_over_Ethernet. ↩ ↩2
-
Electric UI. A deep dive into Single Pair Ethernet. Retrieved 2025-10-28, from https://electricui.com/blog/spe-sensor-node. ↩ ↩2
-
Steffen Graf (2021, Nov). How to Implement an IEEE 802.3cg or 802.3bu Compliant PoDL PSE. Texas Instruments. Retrieved 2025-10-29, from https://www.ti.com/lit/ab/snla395/snla395.pdf. ↩ ↩2
-
Texas Instruments (2022, May). SNLS676 - DP83TC813x-Q1 TC-10 Compliant Small Form Factor 100BASE-T1 Automotive Ethernet PHY [datasheet]. Retrieved 2025-11-05, from https://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/dp83tc813s-q1.pdf. ↩
-
lwIP. Homepage. Retrieved 2024-08-13, from https://savannah.nongnu.org/projects/lwip/. ↩ ↩2