Thermal Management
Thermal Resistance
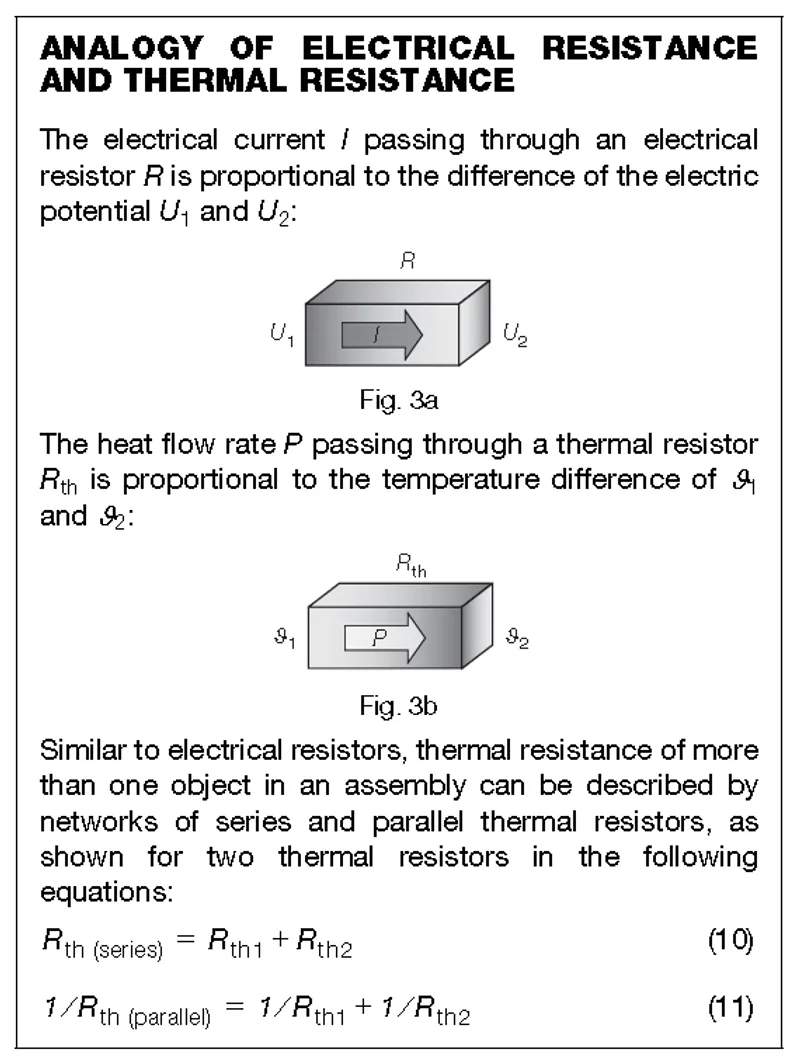
Thermal resistance is way of modelling the thermal behaviour of an object in a way analogous to calculating the current through a resistor by measuring it’s voltage.
The equation is given by:
where:
= Power dissipated by device ()
= Change in temperature between both end-points
= The sum of thermal resistances over which exists
Which is usually expanded (and used) as:
If there is a heatsink involved, a new term is added:
An analogy to electrical resistance…
Inaccuracies In The Thermal Resistance Model
- Thermal resistances assume a linear relationship between temperature and heat flow. This is only a first-order approximation.
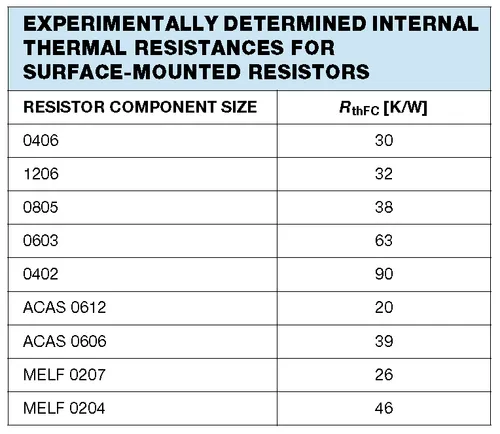
List Of Component Package Thermal Resistances
See the Component Packages page. This has many of the common component packages and their thermal resistances.
Below is a condensed list of experimentally found internal thermal resistances (junction-to-case).