I2C Page Updated
| Date Published: | |
| Last Modified: |
The I2C comms page is now pretty comprehensive with added information about long-distance I2C communication, I2C variants, USB-to-I2C drivers, screenshots of I2C signals, and much more. You can visit it by clicking the link below:
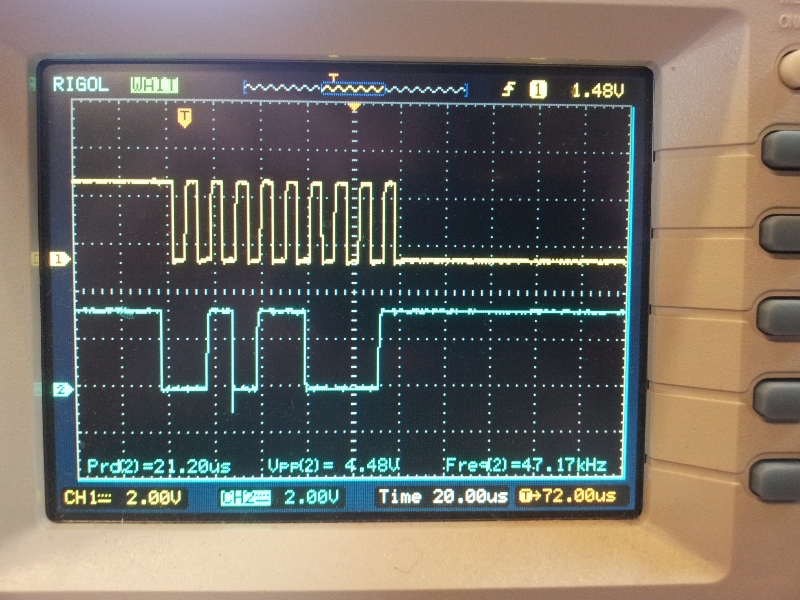
A typical I2C waveform. The top waveform is the clock (SCK), and the bottom waveform is the data (SDA). This shows a master trying to communicate with the slave, but the slave does not acknowledge (the ninth bit is high).
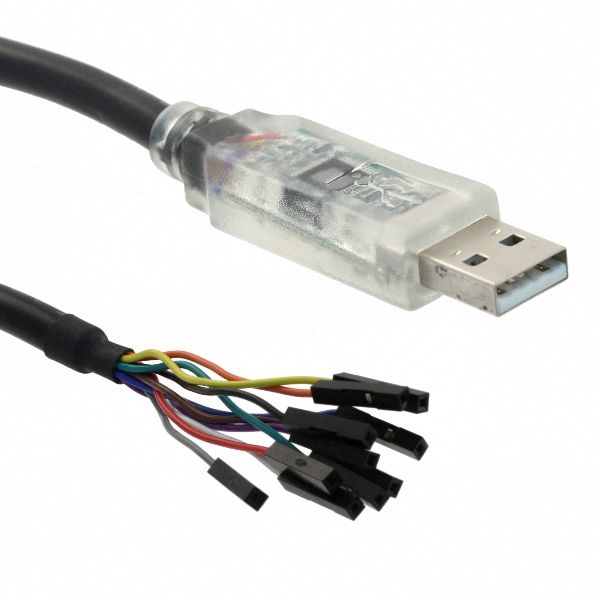

The C232HM-DDHSL-0 FTDI USB-to-MPSSE cable. Creates a bridge between your computer and a number of serial comm protocols such as SPI, I2C and UART.
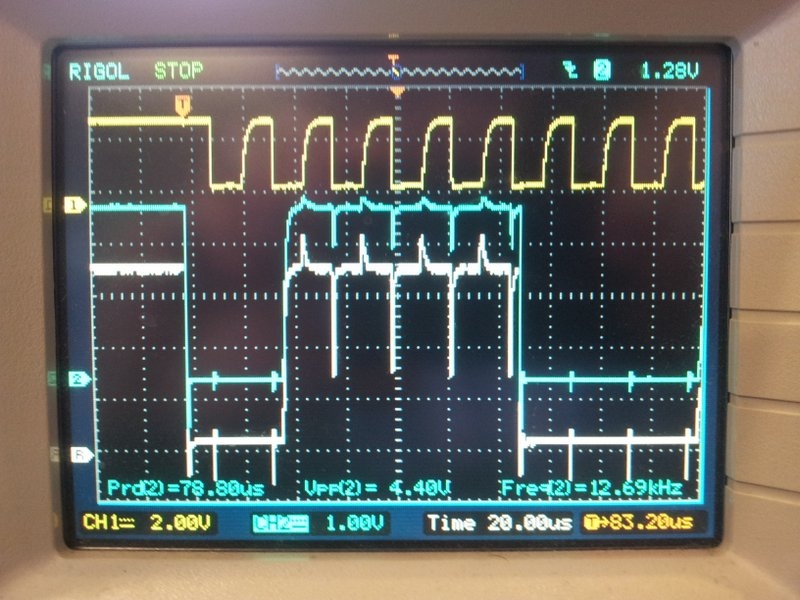
The difference grounding the other wire in a pair makes when transmitting I2C over twisted pair cables. The yellow trace is SCK (for reference), the white trace is SDA with the second wire floating, and the blue trace is SDA when the second wire is either grounded or connected to VCC. Notice a great reduction in cross-coupling on the blue trace. This was over a 20m ethernet cable.
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .



